
Diagram of a Microscope by ScienceDoodles on DeviantArt
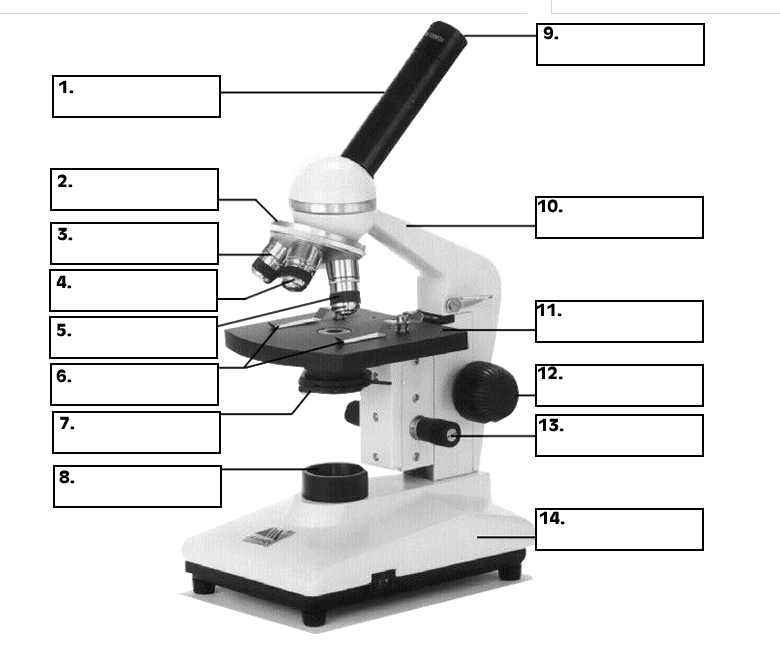
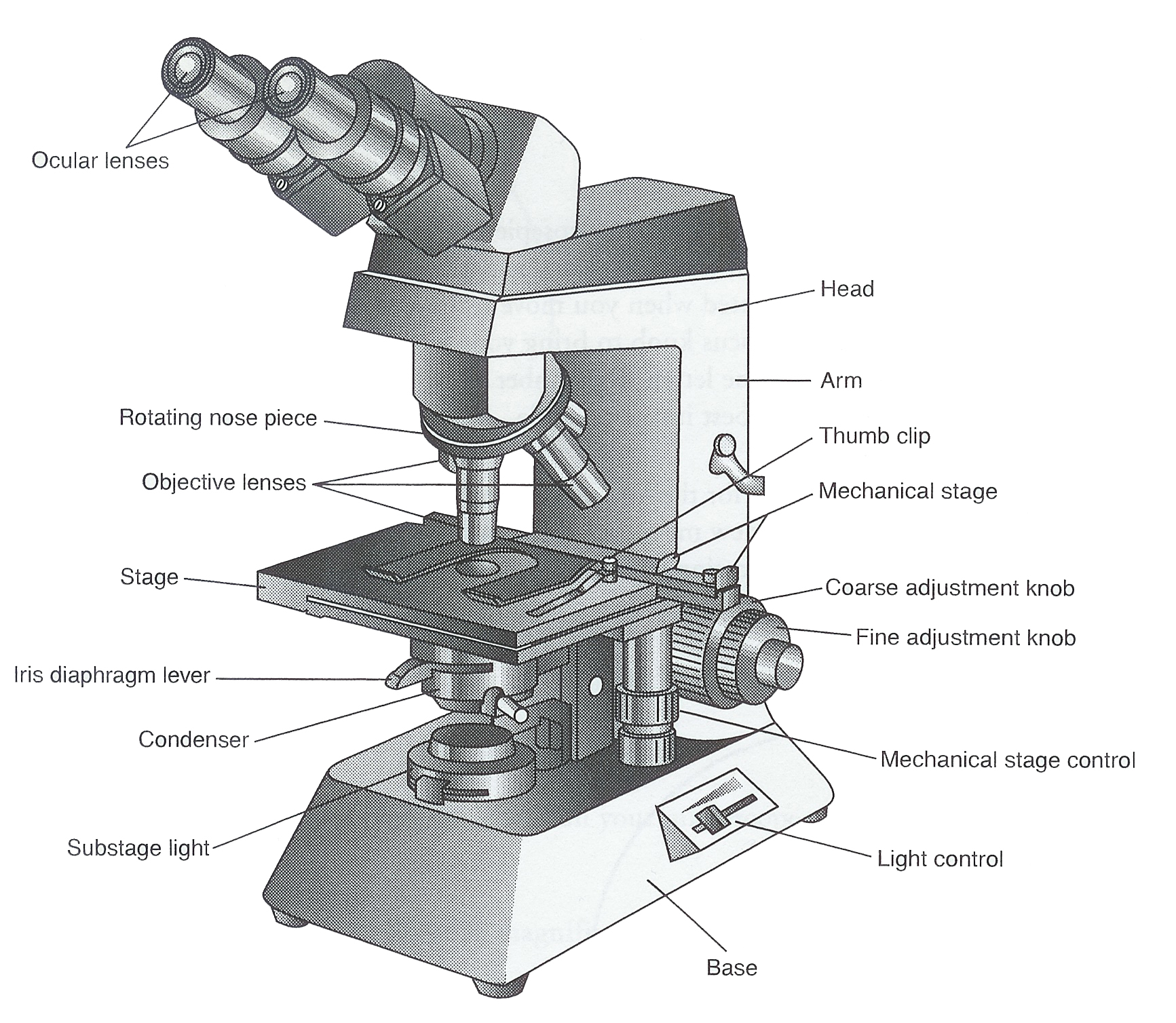
Tube: Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Arm: Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Base: The bottom of the microscope, used for support. Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom.
Microscopes 7th Grade Science
In this interactive, you can label the different parts of a microscope. Use this with the Microscope parts activity to help students identify and label the main parts of a microscope and then describe their functions. Drag and drop the text labels onto the microscope diagram. If you want to redo an answer, click on the box and the answer will.

Microscope Diagram to Print 101 Diagrams
Labeled parts of a microscope. General Rules. Always START and END with the low power lens when putting on OR taking away a slide. Never turn the nose piece by the objective lens. Do not get any portion of the microscope wet - especially the stage and objective lenses.
How to Use a Microscope
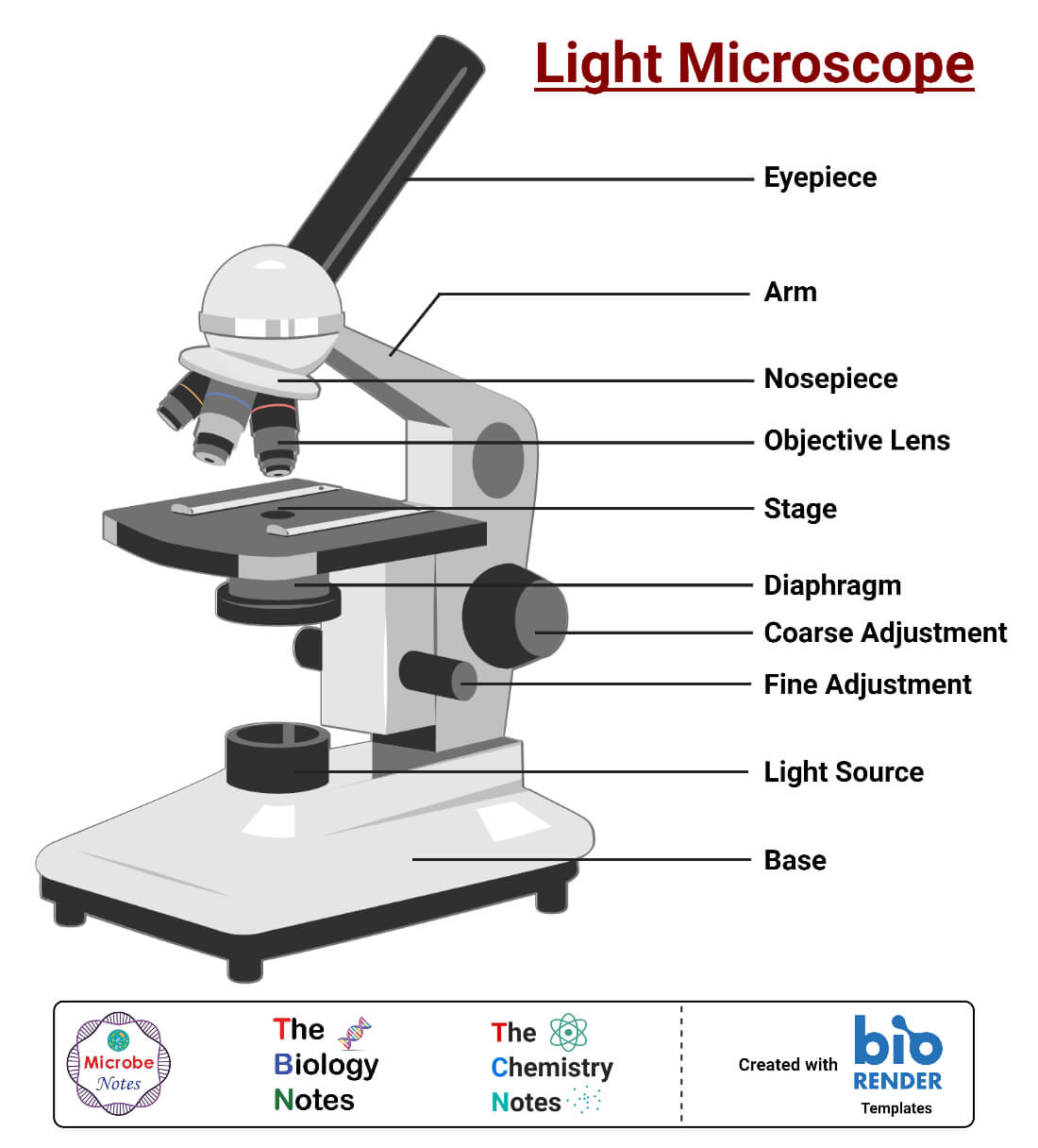
See: Labeled Diagram showing differences between compound and simple microscope parts. Structural Components. The three structural components include. 1. Head. This is the upper part of the microscope that houses the optical parts. 2. Arm . This part connects the head with the base and provides stability to the microscope.

Diagrams of Microscope 101 Diagrams
The web page titled "Parts of a Microscope with Labeled Diagram and Functions" has the following key takeaways: 🔍 The microscope is an essential tool for scientists, researchers, and medical professionals. 🧬 The main function of a microscope is to provide a magnified view of small objects or organisms, such as bacteria, cells, or tissues.
Light Microscope Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram
The description given below summarize the brief description of microscope parts used to visualize the microscopic specimens such as animal cells, plant cells, microbes, bacteria, viruses, microorganisms etc. The Microscopes parts divided into three different structural parts Head, Base, and Arms. Head/Body: It contain the optical parts in the.

Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
Figure: Diagram of parts of a microscope. There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. head, arm, and base. Head - The head is a cylindrical metallic tube that holds the eyepiece lens at one end and connects to the nose piece at other end. It is also called a body tube or eyepiece tube.
Monday September 25 Parts of a Compound Light Microscope
A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram To better understand the structure and function of a microscope, we need to take a look at the labeled microscope diagrams of the compound and electron microscope. These diagrams clearly explain the functioning of the microscopes along with their respective parts.

Microscope Drawing And Label at GetDrawings Free download
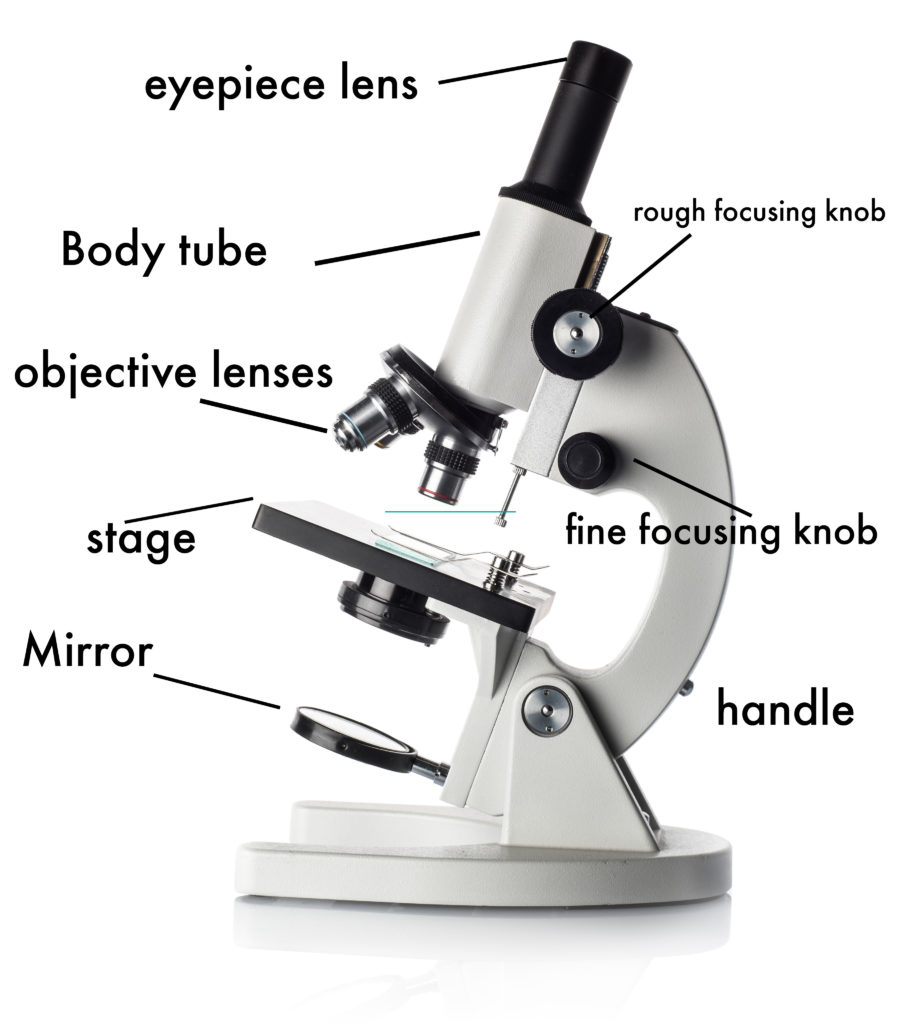
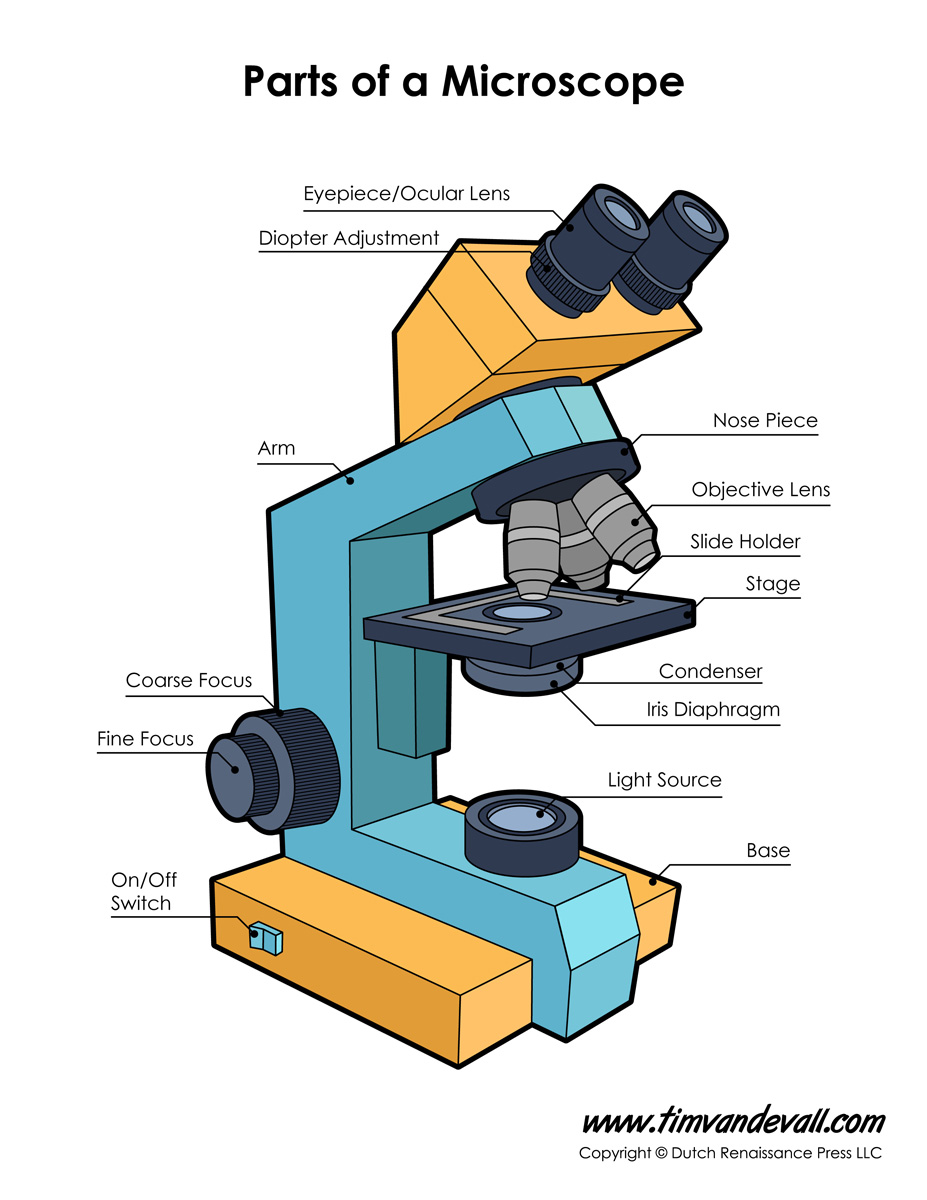
Ocular Lens (eye-piece) Ocular lens of a microscope. It is located at the top of the microscope, and the ocular lens or eyepiece lens is used to look through the specimen. It also magnifies the image formed by the objective lens, usually ten times (10x) or 15 times (15x). Usually, a microscope has an eyepiece of 10x magnification power.
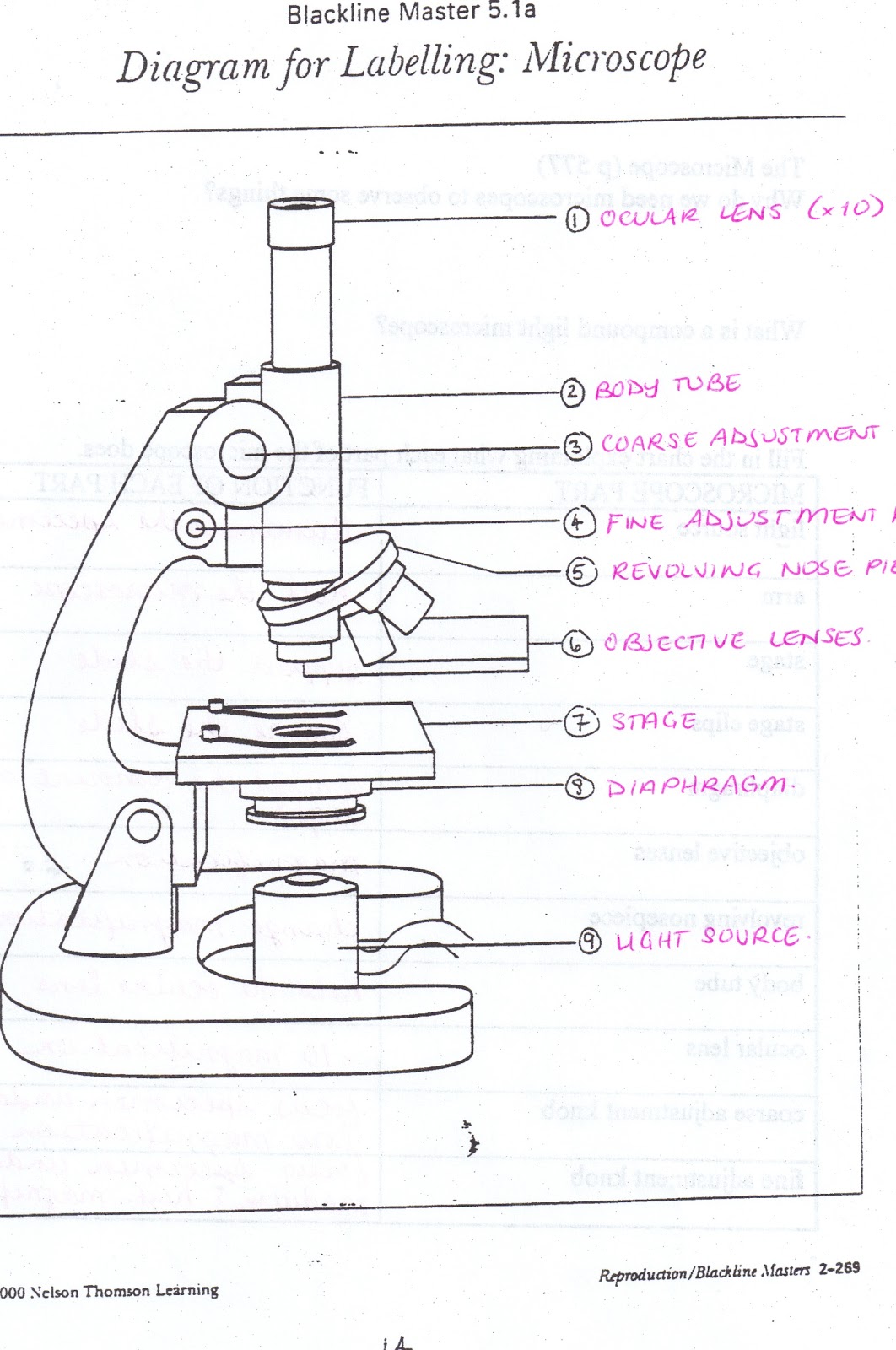
All Saints Online Diagram for Labelling Microscope
Phase-contrast microscope labeled diagram. Phase-contrast microscope functions: Its applications areas include. In cases where the specimen is colorless and is very tiny; In biology to conduct cellular level examination of microorganisms that can't be visualized using the bright field microscopy; Interference Microscope

Microscope Diagram Labeled, Unlabeled and Blank Parts of a Microscope
Eyepiece lens magnifies the image of the specimen. This part is also known as ocular. Most school microscopes have an eyepiece with 10X magnification. 2. Eyepiece Tube or Body Tube. The tube hold the eyepiece. 3. Nosepiece. Nosepiece holds the objective lenses and is sometimes called a revolving turret.
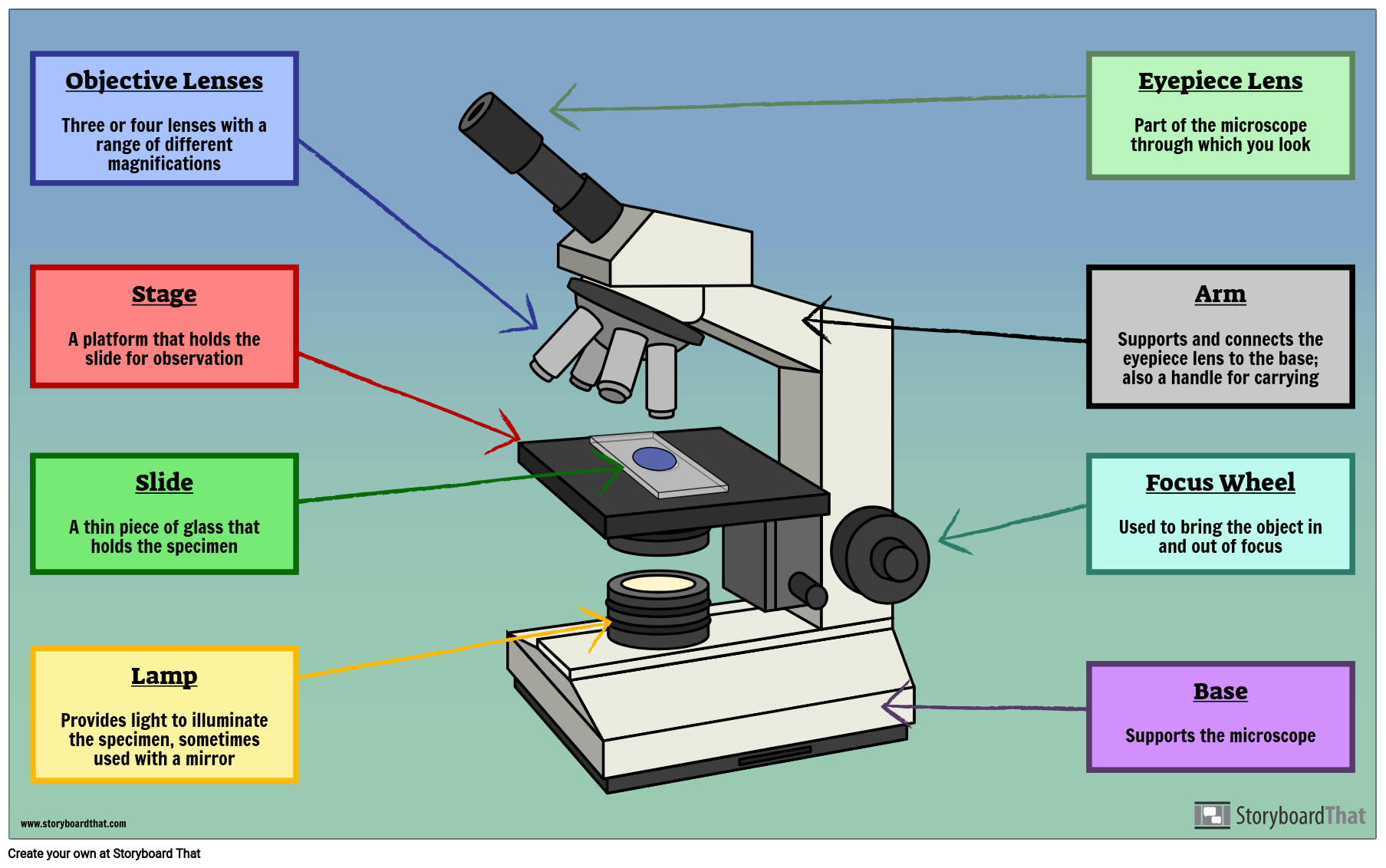
Labelled Microscope with Functions Storyboard by oliversmith
Simple microscope is a magnification apparatus that uses a combination of double convex lens to form an enlarged, erect image of a specimen. The working principle of a simple microscope is that when a lens is held close to the eye, a virtual, magnified and erect image of a specimen is formed at the least possible distance from which a human eye.
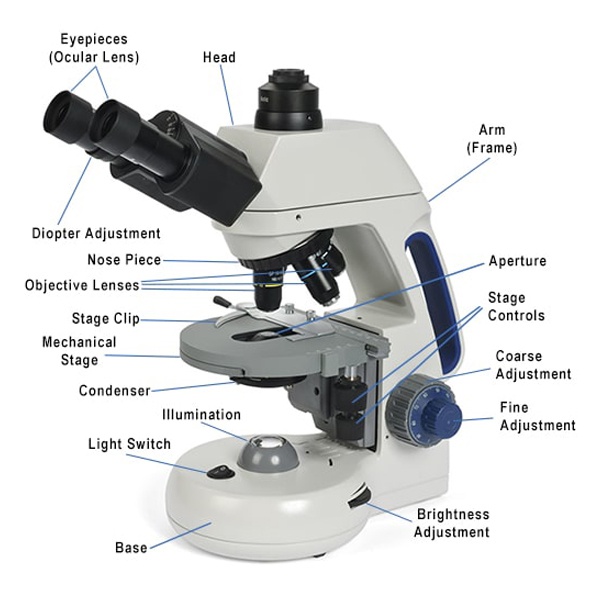
How to Use a Microscope (Properly) Step by Step New York Microscope
Microscope Parts and Functions With Labeled Diagram and Functions How does a Compound Microscope Work?. Before exploring microscope parts and functions, you should probably understand that the compound light microscope is more complicated than just a microscope with more than one lens.. First, the purpose of a microscope is to magnify a small object or to magnify the fine details of a larger.
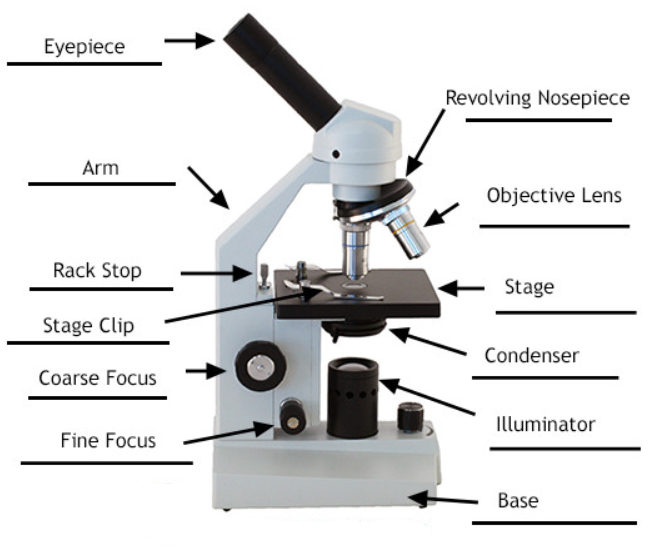
Parts of a Compound Microscope Labeled (with diagrams) Medical
There are two major types of electron microscopy. In scanning electron microscopy ( SEM ), a beam of electrons moves back and forth across the surface of a cell or tissue, creating a detailed image of the 3D surface. This type of microscopy was used to take the image of the Salmonella bacteria shown at right, above.

Microscope Diagram to Print 101 Diagrams
A labeled diagram of microscope parts furnishes comprehensive information regarding their composition and spatial arrangement within the microscope, enabling researchers to comprehend their function effectively. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricate parts of the microscope, exploring their functions in detail..
Ag Biology Unit 2
A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.